It’s no secret that modern medical professionals rely heavily on digital records to access information. However, sharing and accessing health data between systems has created a challenge for healthcare. By its nature, health data is sensitive and requires stringent privacy and security precautions. Yet, if providers struggle to access it, there can be serious consequences for patients.
That's why Interoperability is recognized as "The White Elephant in the Room" among healthcare professionals. Today in our journey to better understand the software challenges in the healthcare industry, we’re going to look at the problem of interoperability in healthcare software.
What is Interoperability?
Interoperability is the ability of different software applications, devices, and systems to communicate information with one another. Anytime you send a text message to a friend with a different provider or a doctor refers you to a specialist, you’re experiencing interoperability in action. It’s what makes the digital world so easy to navigate.
To achieve interoperability, a system or device must be able to convert data into a format that the receiving system can understand. This is what is known as semantic interoperability. It allows systems of different formats and languages to communicate without losing information in translation.
An efficient interoperability system provides the necessary information infrastructure for a seamless and secure exchange of data.
To achieve interoperability, healthcare providers must adopt and optimize electronic health records (EHRs) and health information exchange (HIE) services. Paper health records, used until recently by most doctors and hospitals, can only be used by one person at a time in any given location.
As the healthcare industry evolves, the providers network also increases, different entities combining and sharing amounts of information with each other, from medical history, insurance information, billing platforms, drug inventories, and so on.
Electronic files allow information to be exchanged and used simultaneously and securely by authorized users from multiple locations, leading to better coordination of care.
Why is Interoperability Important in the Healthcare Industry?
This ability to transfer data has become essential for many industries to utilize a range of software solutions. It allows companies to easily gather data, and utilize it to achieve their goals. The same is true for providers in the healthcare industry.
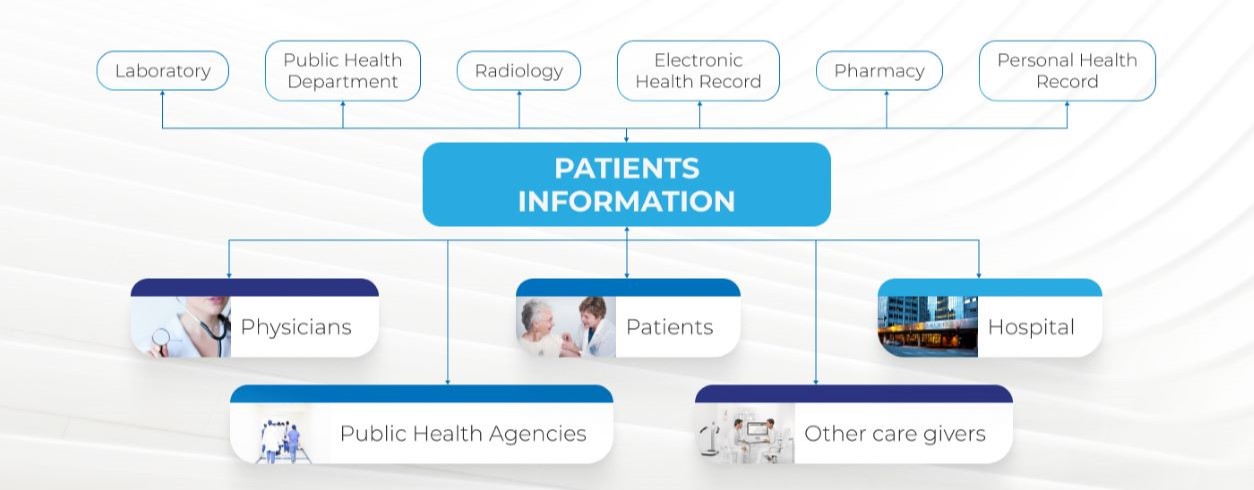
In the health digital environment, interoperability connects individuals, processes, and systems connect a plethora of health information data. Patients, providers, hospitals, and other significant stakeholders are all involved in the creation, exchange, and use of healthcare data.
Many doctors rely on interoperability between systems both in-house and from other providers to attain patient health records. Without this information, mistakes that could cost other industries money could cost lives in healthcare.
Additionally, this same ability to transfer data between systems is often used when medical professionals wish to make a referral. Without it, providers must transcribe information manually. As a result, it can be difficult for any specialists to get comprehensive medical records to provide the best care they can.
However, despite the gravity of its importance, interoperability continues to prove a challenge for the healthcare industry.
Levels of Interoperability in Healthcare
The Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society has defined four levels of interoperability in healthcare.
Foundational
This most basic level of interoperability is also known as simple transport. Data at this level is transferred between software or devices without interpretation or transformation.
Structural
Also known as structured transport, this level is when all data is standardized to a particular format to be interpreted by multiple systems. This helps records to remain consistent, easy to transfer, and centralized.
Semantic
This level of interoperability can be difficult to achieve. Semantic transport involves the exchange of data between systems with totally different data formats. However, as different devices have different ways of presenting information, this can be difficult to achieve.
Organizational
This level involves the seamless exchange of data between organizations with different formats and regulations. This requires software and policy innovations. It is almost the most difficult to achieve.
Types of Interoperability Architecture in Healthcare
Network architecture for health information across software and devices primarily comes in three forms.
Centralized
In this system, data is collected and stored in a centralized database. This form of exchange organization operates with complete control over the data stored including the ability to authenticate and authorize exchanges.
Decentralized - Data
in this system is stored in connected but independent databases for data sharing and exchange.
Hybrid
These systems take many forms as they are variations of both decentralized and centralized interoperability systems to take on the advantages of both. These are also increasingly common as more services are implemented
Alongside these systems, healthcare APIs have recently emerged. APIs outline specifications that allow for software applications to build on data and functionality from another without a complete interpretation.
Why Interoperability is a Challenge in the Healthcare Industry
Like other industries, the healthcare industry relies on various digital resources that allow them to access patients’ medical records, refer patients to specialists, and more. Yet, the diverse software systems in the healthcare industry struggle to effectively and consistently communicate, making it difficult for providers to achieve a comprehensive picture of their patients’ records. So, let’s take a look at the issues that prevent interoperability in the healthcare industry.
Poor Standardization
Despite the emerging standard formats such as FHIR, Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources, many providers still use custom electronic health records, EHRs, to store and share information in-house. Whereas these formats were revolutionary when they were first introduced, providers now struggle to share this information between new systems and other providers.
This poor standardization prevents effective interoperability and requires healthcare providers looking to make old EHRs compatible with new systems with help from software development companies.
Security
Patient healthcare records and related information are subject to stringent compliance and regulation. Therefore, the storage and transfer of this data require serious security measures to prevent potential data breaches. Even a small leak of patient information could result in serious legal penalties and fees for the provider found responsible.
As interoperability is dependent on the movement of data, these security demands create a serious hindrance.
That is why those in the healthcare industry looking to improve interoperability in-house and between providers must seek development solutions that understand the delicate nature of healthcare data.
Legacy Systems
Naturally, older systems exist in every industry, and healthcare is no exception. Consequently, these systems often fail to integrate with no solutions, let alone meet interoperability requirements. As such, legacy systems offer a dual-edged problem for providers.
To counter this, a healthcare organization's best option is to pursue a software solution that integrates legacy systems while making the data stored within more accessible. As interoperability is dependent on the movement of data, these security demands create a serious hindrance. That is why those in the healthcare industry looking to improve interoperability in-house and between providers must seek development solutions that understand the delicate nature of healthcare data.
Budget Limits
Building a truly interoperable system takes time, resources, and money. This prevents many healthcare providers, especially independent practitioners, from upgrading their existing systems.
The best option to overcome this challenge is to work with software development companies capable of offering affordable solutions without sacrificing quality such as a nearshore company.
How KNDCODE Can Help
Interoperability is essential for healthcare providers to access information and provide the best care possible. However, it must be addressed with careful consideration and software expertise. To that end, take a look at what KNDCODE’s nearshore software development can do for you. Work with a team that understands the sensitive software needs of the healthcare industry, including the interoperability of software.
KNDCODE’s team of certified software development professionals have the knowledge and the skills to help you make your systems fully interoperable. With over 20 years of experience in the field, KNDCODEs experts can assist with IT consulting, nearshore custom software development, software engineering, application integrations, mobile applications, and more.
Contact KNDCODE today for more information about improving your legacy software’s interoperability.
KNDCODE, Always Ahead, Forward, Near.
Ebooks
KNDCODE'S eBooks your gateway to knowledge and expertise in software development. Our curated collection of insightful and practical eBooks covers a wide range of topics, helping you enhance your skills and unlock your full potential. Our free eBooks provide valuable insights, best practices, and real-world solutions to empower your career in the ever-changing world of software development.

KNDCODE Credentials
Solutions to the most complex operational challenges.Learn more about our capabilities.
Read more
Hiring Guide (Dev)
Have access to the complete guide to effective Software Development hiring
Read more
Software Development Myths
Here are 8 common software myths and the truth behind each of them.
Read more
Nearshore vs Offshore SD
Nearshore vs Offshore Software Development. What's the difference?
Read more





